
Introduction
Digital dentistry encompasses a wide array of technologies that have been under development for several decades. Tools such as Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), intraoral scanners, 3D printing, CNC milling, and navigation systems have revolutionized the field by providing detailed insights and precise tools for treatment planning and execution. Early adopters of these technologies encountered significant challenges, primarily due to compatibility issues among different data formats and systems. However, continuous
Digital dentistry encompasses a wide array of technologies that have been under development for several decades. Tools such as Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), intraoral scanners, 3D printing, CNC milling, and navigation systems have revolutionized the field by providing detailed insights and precise tools for treatment planning and execution. Early adopters of these technologies encountered significant challenges, primarily due to compatibility issues among different data formats and systems. However, continuous
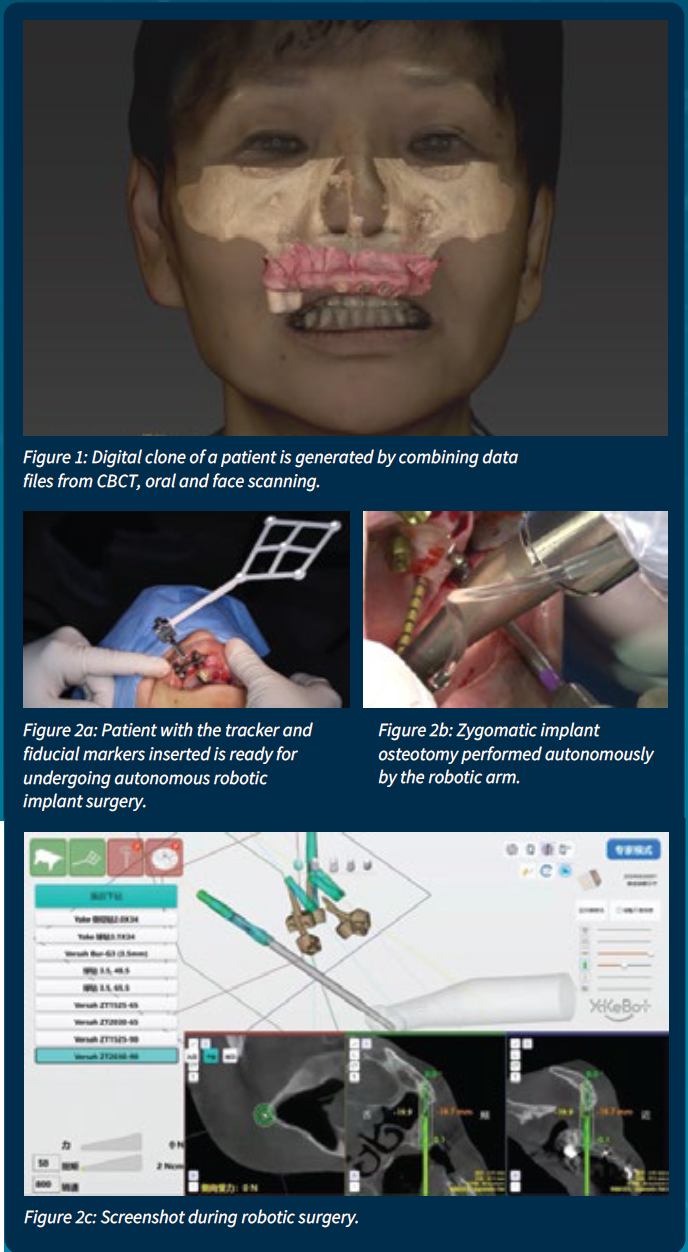
advancements have largely resolved these compatibility issues, leading to more integrated and cohesive digital workflows. Nowadays, the seamless integration of CBCT, oral and face-scanning files can easily generate a life-like digital clone of the patient (Figure 1). As digital technologies
continue to evolve, their penetration rates are gradually increasing. For instance, a panel survey conducted by the American Dental Association in 2021 revealed that 53% of respondents had integrated intraoral scanners into their practices (ref1).
While existing technologies are increasingly adopted by clinicians, new technologies are being developed and introduced to the dental community. Notably, two technological advancements—Robotics and Artificial Intelligence (AI)—have recently made significant impacts on digital dentistry.
Robotics (ref 2-4)
Robotics is revolutionizing dental implant surgery by
While existing technologies are increasingly adopted by clinicians, new technologies are being developed and introduced to the dental community. Notably, two technological advancements—Robotics and Artificial Intelligence (AI)—have recently made significant impacts on digital dentistry.
Robotics (ref 2-4)
Robotics is revolutionizing dental implant surgery by
enhancing precision, efficiency, and patient outcomes.
Advanced robotic systems can now assist surgeons in
planning and executing implant procedures with
unprecedented accuracy (Figure 2a-c). These robots utilize 3D imaging and AI-powered software to create detailed surgical plans, determining optimal implant placement based on the patient's unique anatomy. During surgery, robotic arms can guide the dentist's movements or even perform certain
aspects of the procedure autonomously, minimizing human
error and reducing invasiveness. This technology facilitates
smaller incisions, faster recovery times, and more predictable
results. Additionally, robotics enables complex procedures to
be performed more consistently, potentially making advanced
dental implant treatments accessible to a broader range of
patients and practitioners.
Since 2017, robotic systems for dental implantology, such as
Since 2017, robotic systems for dental implantology, such as
YOMI by Neocis and Yakebot by YakeBot (Beijing) Technology
Co., Ltd., has been introduced in America and China. Robotic
surgery can be categorized into six different levels of
autonomy based on the degree of control exerted by the robot
versus the human surgeon. These levels range from complete
human control to full robotic automation. Most FDA-cleared
surgical robots are currently at Level 1, with some reaching
Levels 2 and 3 autonomy. For example, YOMI belongs to the
level 2 whereas Yakebot is level 3. The trend is toward
increasing levels of autonomy in surgical robotics, but
regulatory frameworks and safety considerations are still
evolving to keep pace with these advancements.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Challenges and Future Prospects


